Modules | |
| Linear Algebra | |
| Optimisation | |
| This module contains optimisation methods for Newton type optimisation. | |
Classes | |
| class | go3Vector< T > |
| 3-dimensional vector. More... | |
| class | goBiorthoWavelet |
| class | goComplex< T > |
| Complex number class. More... | |
| class | goMath::CubicSpline< T > |
| Cubic interpolating splines. More... | |
| class | goMath::CubicSplineND< T > |
| Cubic interpolating splines. More... | |
| class | goCurve< T > |
| Curve representation. More... | |
| class | goSignal::TVL1 |
| TV-regularised L1-norm approximation of an image after [1]. More... | |
| class | goMath::GaussPDF< input_type, output_type > |
| Gauss' probability density function. More... | |
| class | goMath::MultiGaussPDF< input_vector, scalar_type > |
| Vector values Gauss distribution. More... | |
| class | goMath::Manifold< element_type, tangent_type > |
| Interface for manifolds. More... | |
| class | goMath::SO3< T > |
| Rotation group. More... | |
| class | goMath::LinearSpace< T > |
| Simple linear vector space. More... | |
| class | goMath::UnitSphere< T > |
| Unit sphere. More... | |
| class | goMath::PDF< input_type, output_type > |
| Probability density function base template. More... | |
| class | goPointCloud< T > |
| Point cloud. More... | |
| class | goQuaternion< T > |
| Quaternion class. More... | |
| class | goSparseMatrix |
| Basic sparse matrix class with Matlab mxArray support. More... | |
| class | goMath::ThinSVD< Real > |
Typedefs | |
| typedef go4Vector< goFloat > | go4Vectorf |
| 4-dimensional vector. More... | |
| typedef go4Vector< goDouble > | go4Vectord |
| typedef goCurve< goFloat > | goCurvef |
| typedef goCurve< goDouble > | goCurved |
| typedef goPointCloud< goFloat > | goPointCloudf |
Enumerations | |
| enum | { UNSORTED, ROW_WISE, COLUMN_WISE } |
Functions | |
| template<class iterator_type , class manifold_type > | |
| bool | goMath::karcherMean (iterator_type start, int count, manifold_type &manifold, typename manifold_type::Element &meanRet, int max_iterations=1000, double epsilon=1e-6) |
| Karcher mean for generic Riemannian manifolds. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| T | goMath::mod (T value, T modulus) |
| Modulus function. More... | |
| template<class Real > | |
| Real | goMath::abs (Real a) |
| template<class Real > | |
| Real | goMath::hypot (const Real &a, const Real &b) |
| template<class Real > | |
| Real | goMath::acos (const Real &a) |
| template<class Scalar > | |
| Scalar | goMath::min (Scalar a, Scalar b) |
| template<class Scalar > | |
| Scalar | goMath::max (Scalar a, Scalar b) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | goMath::max (const goFixedArray< T > &a) |
| template<class T > | |
| goSize_t | goMath::maxIndex (const goFixedArray< T > &a) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | goMath::min (const goFixedArray< T > &a) |
| template<class T > | |
| goSize_t | goMath::minIndex (const goFixedArray< T > &a) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | goMath::maxabs (const goFixedArray< T > &a) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | goMath::minabs (const goFixedArray< T > &a) |
| goSparseMatrix::goSparseMatrix (int rows=0, int cols=0) | |
| void | goSparseMatrix::init () |
| void | goSparseMatrix::setSize (int rows, int cols) |
| void | goSparseMatrix::set (int row, int col, double value) |
| Not implemented. More... | |
| int | goSparseMatrix::getElementCount () const |
| Get the total number of nonzero elements. More... | |
| int | goSparseMatrix::getSortType () const |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::fillBegin (int elementCount) |
| Begin filling elementCount elements in this matrix. More... | |
| int | goSparseMatrix::fillNext (int row, int col, double value) |
| Fills the next element in this matrix. More... | |
| void | goSparseMatrix::fillEnd (int sortType=ROW_WISE) |
| Ends filling the matrix. More... | |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::matrixVectorMult (goArray< goDouble > &ret, const goArray< goDouble > &v) |
| (this) * v More... | |
| template<class Tv > | |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::matrixVectorMult (goMath::Vector< Tv > &ret, const goMath::Vector< Tv > &v) |
| (this) * v More... | |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::vectorMatrixMult (goArray< goDouble > &ret, const goArray< goDouble > &v) |
| v' * (this) More... | |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::matrixVectorMult (goSparseMatrix &ret, const goArray< goDouble > &v) |
| (this) * v More... | |
| template<class Tv > | |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::matrixVectorMult (goSparseMatrix &ret, const goMath::Vector< Tv > &v) |
| (this) * v More... | |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::vectorMatrixMult (goSparseMatrix &ret, const goArray< goDouble > &v) |
| v' * (this) More... | |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::matrixMatrixMult (goSparseMatrix &ret, goSparseMatrix &m) |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::matrixMatrixAdd (goSparseMatrix &ret, goSparseMatrix &m) |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::matrixMatrixSubtract (goSparseMatrix &ret, goSparseMatrix &m) |
| goSparseMatrix & | goSparseMatrix::operator*= (goDouble scalar) |
| goSparseMatrix | goSparseMatrix::operator* (const goSparseMatrix &other) const |
| template<class Tv > | |
| goMath::Vector< Tv > | goSparseMatrix::operator* (const goMath::Vector< Tv > &v) const |
| goSparseMatrix | goSparseMatrix::operator* (goDouble s) const |
| goSparseMatrix | goSparseMatrix::operator+ (const goSparseMatrix &m) const |
| goSparseMatrix | goSparseMatrix::operator- (const goSparseMatrix &m) const |
| goIndex_t | goSparseMatrix::row (goIndex_t elementIndex) const |
| Returns the row of the element at elementIndex. | |
| goIndex_t | goSparseMatrix::column (goIndex_t elementIndex) const |
| Returns the row of the element at elementIndex. | |
| goDouble | goSparseMatrix::value (goIndex_t elementIndex) const |
| Returns the value of the element at elementIndex. | |
| int | goSparseMatrix::getRowCount () const |
| Returns the number of rows. | |
| int | goSparseMatrix::getColumnCount () const |
| Returns the number of columns. | |
| const goArray< goIndex_t > & | goSparseMatrix::getRowStart () const |
| For row-sorted matrices. | |
| const goArray< goIndex_t > & | goSparseMatrix::getColStart () const |
| For column-sorted matrices. | |
| void | goSparseMatrix::sortRows (bool sort_columns=false) |
| Sorts in ascending row order. More... | |
| void | goSparseMatrix::sortColumns (bool sort_rows=false) |
| Sorts in ascending column order. More... | |
| void | goSparseMatrix::findRows () |
| void | goSparseMatrix::findColumns () |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::appendRow (const goSparseMatrix &r) |
| Appends the row matrix r to this matrix. More... | |
| bool | goSparseMatrix::appendRows (const goSparseMatrix &m) |
| void | goSparseMatrix::transpose () |
| goArray< goIndex_t > & | goSparseMatrix::getColIndex () |
| const goArray< goIndex_t > & | goSparseMatrix::getColIndex () const |
| goArray< goIndex_t > & | goSparseMatrix::getRowIndex () |
| const goArray< goIndex_t > & | goSparseMatrix::getRowIndex () const |
| goArray< goDouble > & | goSparseMatrix::getValues () |
| const goArray< goDouble > & | goSparseMatrix::getValues () const |
| void | goSparseMatrix::setSortType (int t) |
| template<class T > | |
| bool | goMath::euclideanToBarycentric (const goMath::Matrix< T > &simplex, const goMath::Vector< T > &point, goMath::Vector< T > &ret) |
| Convert euclidean to barycentric coordinates. More... | |
| template<class MatrixType , class VectorType > | |
| goDouble | goMath::goConjugateGradients (const MatrixType &A, const VectorType &b, VectorType &x, goDouble epsilon=1e-6) |
| Conjugate gradients solver. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| bool | goMath::resampleCubic (const goMath::Matrix< T > &source, goMath::Matrix< T > &target, goSize_t resamplePointCount, bool closed=false, goFixedArray< goDouble > *accumLength_=0) |
| Piecewise cubic resampling of a curve represented by a configuration matrix. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| void | goMath::resampleLinear (const goFixedArray< T > &f, goFixedArray< T > &ret) |
| bool | goMath::laplacian2D (const goSignal3DBase< void > &sig, goSignal3DBase< void > &retValue) |
| Calculates the laplacian (2nd derivative) of a 2D signal (z-size == 1). More... | |
| bool | goMath::gradient2D (const goSignal3DBase< void > &sig, goSignal3DBase< void > &retValue) |
| Calculates the gradient of a 2D signal (z-size == 1). More... | |
| bool | goMath::ddx2D (const goSignal3DBase< void > &sig, goSignal3DBase< void > &retValue) |
| Calculates the derivative in x direction assuming a 2D signal. More... | |
| bool | goMath::ddy2D (const goSignal3DBase< void > &sig, goSignal3DBase< void > &retValue) |
| Calculates the derivative in y direction assuming a 2D signal. More... | |
| bool | goMath::centralDifferences (const goSignal3DBase< void > &x, goSignal3DBase< void > &retValue, int dimension=0, goDouble h=1.0, const goSignal3DBase< void > *mask=0) |
| Calculate central finite differences in a given direction. More... | |
| bool | goMath::forwardDifferences (const goSignal3DBase< void > &x, goSignal3DBase< void > &retValue, int dimension=0, goDouble h=1.0, const goSignal3DBase< void > *mask=0) |
| Calculate forward finite differences in a given direction. More... | |
| bool | goMath::backwardDifferences (const goSignal3DBase< void > &x, goSignal3DBase< void > &retValue, int dimension=0, goDouble h=1.0, const goSignal3DBase< void > *mask=0) |
| Calculate backward finite differences in a given direction. More... | |
| bool | goMath::curvatureDirect2D (const goSignal3DBase< void > &input, goSignal3D< void > &result, goDouble hx=1.0, goDouble hy=1.0) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | goMath::integrate (const goMath::Vector< T > &v) |
| Sehnentrapezformel. Step width (h) is assumed 1, so normalisation may be needed afterwards. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| T | goMath::integrateSimpson (const goMath::Vector< T > &v) |
| Integration with Simpson rule. Step width h is assumed 1, so normalisation may be needed afterwards. More... | |
| template<class T > | |
| T | goMath::integrateSum (const goMath::Vector< T > &v) |
| template<class T > | |
| T | goMath::stencil (const goSignal3DBase< void > &sig, const goMath::Matrix< T > &s) |
Calculate 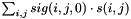 . More... . More... | |
| void | goMath::transform2D (const goSignal3DBase< void > &source, goDouble scale, goDouble angle, goDouble t_x, goDouble t_y, goSignal3D< void > &target, bool setsize=true) |
| 2D euclidean transformation of an image. More... | |
| void | goMath::scale2D (const goSignal3DBase< void > &source, goSignal3DBase< void > &target, bool keep_aspect=false) |
Scale source into target. More... | |
| void | goMath::paste2D (const goSignal3DBase< void > &source, goDouble scale, goDouble angle, goDouble t_x, goDouble t_y, goSignal3DBase< void > &target, goFloat bgColour) |
Paste source at under some euclidean transformations into target. More... | |
Detailed Description
Typedef Documentation
◆ go4Vectorf
| typedef go4Vector<goFloat> go4Vectorf |
4-dimensional vector.
- Todo:
- make this a descendant of goMath::Vector, fix size to 4, provide x,y,z,t/w as references.
Function Documentation
◆ abs()
| Real goMath::abs | ( | Real | a | ) |
- Returns
- the absolute value of a real (no-complex) scalar.
◆ acos()
| Real goMath::acos | ( | const Real & | a | ) |
::acos seems to result in nan when the argument is exactly 1.0 (contrary to the manpage!). That is caught here.
- Returns
- acos (a)
◆ appendRow()
|
inline |
Appends the row matrix r to this matrix.
The result is [(*this)' r']'
- Parameters
-
r Must be of size (1, this->getColumnCount())
- Returns
- True if successful, false otherwise.
◆ appendRows()
|
inline |
- Bug:
- After appending rows, findRows() should be called when this matrix is row-sorted. This needs to be fixed or it will lead to misunderstandings and malfunctioning code/hard to find errors.
◆ backwardDifferences()
| bool goMath::backwardDifferences | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | x, |
| goSignal3DBase< void > & | retValue, | ||
| int | dimension = 0, |
||
| goDouble | h = 1.0, |
||
| const goSignal3DBase< void > * | mask = 0 |
||
| ) |
Calculate backward finite differences in a given direction.
- Parameters
-
x Data grid. retValue Contains finite differences after the function returns true. If the size of retValue does not match the size of x and retValue is a goSignal3D<void>, retValue will be resized to the size of x, including number of channels, blocksize of x and border of 1 in each direction. dimension Dimension (0, 1, or 2 for x, y, or z) h Grid spacing (default 1) mask Optional mask of type goInt8. If given, central differences are only calculated where mask is != 0. The other values in retValue are not changed. Default: NULL.
- Note
- Only goFloat and goDouble data are supported. The data types of x and retValue may differ. Both are given by the user, so the data type of retValue must be set before calling this function. It may be of wrong size, in which case it must point to a goSignal3D<void> in order for it to be resizable.
- The algorithm is run for all channels.
- Returns
- True if successful, false otherwise.
◆ centralDifferences()
| bool goMath::centralDifferences | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | x, |
| goSignal3DBase< void > & | retValue, | ||
| int | dimension = 0, |
||
| goDouble | h = 1.0, |
||
| const goSignal3DBase< void > * | mask = 0 |
||
| ) |
Calculate central finite differences in a given direction.
- Parameters
-
x Data grid. retValue Contains finite differences after the function returns true. If the size of retValue does not match the size of x and retValue is a goSignal3D<void>, retValue will be resized to the size of x, including number of channels, blocksize of x and border of 1 in each direction. dimension Dimension (0, 1, or 2 for x, y, or z) h Grid spacing (default 1) mask Optional mask of type goInt8. If given, central differences are only calculated where mask is != 0. The other values in retValue are not changed. Default: NULL.
- Note
- Only goFloat and goDouble data are supported. The data types of x and retValue may differ. Both are given by the user, so the data type of retValue must be set before calling this function.
- The algorithm is run for all channels.
- Returns
- True if successful, false otherwise.
◆ ddx2D()
| bool goMath::ddx2D | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | sig, |
| goSignal3DBase< void > & | retValue | ||
| ) |
Calculates the derivative in x direction assuming a 2D signal.
This function calculates the derivative in x-direction while assuming the signal is 2-dimensional. The arguments are restricted to signals of type GO_FLOAT and GO_DOUBLE.
- Todo:
- Implement for 3D-signals.
- Parameters
-
sig Signal to calculate the derivative of. retValue After the function returned true, contains the x-derivative of sig. Must be of the same size as sig.
- Returns
◆ ddy2D()
| bool goMath::ddy2D | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | sig, |
| goSignal3DBase< void > & | retValue | ||
| ) |
Calculates the derivative in y direction assuming a 2D signal.
This function calculates the derivative in y-direction while assuming the signal is 2-dimensional. The arguments are restricted to signals of type GO_FLOAT and GO_DOUBLE.
- Todo:
- Implement for 3D-signals.
- Parameters
-
sig Signal to calculate the derivative of. retValue After the function returned true, contains the y-derivative of sig. Must be of the same size as sig.
- Returns
◆ euclideanToBarycentric()
| bool goMath::euclideanToBarycentric | ( | const goMath::Matrix< T > & | simplex, |
| const goMath::Vector< T > & | point, | ||
| goMath::Vector< T > & | ret | ||
| ) |
Convert euclidean to barycentric coordinates.
This works only for vertices with n+1 points in n dimensions.
- Parameters
-
simplex Simplex points, one point per column point Point in euclidean coordinates ret On return, contains barycentric coordinates of point.
- Returns
- True if successful, false otherwise (also check log).
◆ fillBegin()
|
inline |
Begin filling elementCount elements in this matrix.
The actual amount of elements filled in can be lower than elementCount. Do not forget to call fillEnd() when done filling in values.
- Parameters
-
elementCount Maximum number of elements to be filled in.
- Returns
- True if successful, false otherwise.
◆ fillEnd()
|
inline |
Ends filling the matrix.
Ends filling and resizes the internal arrays according to the number of elements filled in.
◆ fillNext()
|
inline |
Fills the next element in this matrix.
- Parameters
-
row Row of the element col Column of the element value Value of the element
- Returns
- Number of elements that can still be filled in after this call. If zero, all subsequent calls to fillNext() will not change the matrix.
◆ forwardDifferences()
| bool goMath::forwardDifferences | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | x, |
| goSignal3DBase< void > & | retValue, | ||
| int | dimension = 0, |
||
| goDouble | h = 1.0, |
||
| const goSignal3DBase< void > * | mask = 0 |
||
| ) |
Calculate forward finite differences in a given direction.
- Parameters
-
x Data grid. retValue Contains finite differences after the function returns true. If the size of retValue does not match the size of x and retValue is a goSignal3D<void>, retValue will be resized to the size of x, including number of channels, blocksize of x and border of 1 in each direction. dimension Dimension (0, 1, or 2 for x, y, or z) h Grid spacing (default 1) mask Optional mask of type goInt8. If given, central differences are only calculated where mask is != 0. The other values in retValue are not changed. Default: NULL.
- Note
- Only goFloat and goDouble data are supported. The data types of x and retValue may differ. Both are given by the user, so the data type of retValue must be set before calling this function. It may be of wrong size, in which case it must point to a goSignal3D<void> in order for it to be resizable.
- The algorithm is run for all channels.
- Returns
- True if successful, false otherwise.
◆ getElementCount()
|
inline |
Get the total number of nonzero elements.
nnz() in Matlab.
- Returns
- Number of nonzero elements.
◆ goConjugateGradients()
| goDouble goMath::goConjugateGradients | ( | const MatrixType & | A, |
| const VectorType & | b, | ||
| VectorType & | x, | ||
| goDouble | epsilon = 1e-6 |
||
| ) |
Conjugate gradients solver.
Conjugate gradients method for solving linear equation systems.
Solves A*x=b iteratively for x.
- Note
- Currently implemented for goSparseMatrix and goMath::Vector.
- Returns
- final abs(A*x-b).
Finde einen Vektor x fuer A*x=b. Geht momentan nur fuer goSparseMatrix.
- Todo:
- Spezialimplementierung fuer goSparseMatrix (gibts schon) und Standardimplementierung fuer andere Matrizen.
- Returns
- Error.
◆ gradient2D()
| bool goMath::gradient2D | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | sig, |
| goSignal3DBase< void > & | retValue | ||
| ) |
Calculates the gradient of a 2D signal (z-size == 1).
- Note
- The data type of the arguments is currently restricted to GO_FLOAT and GO_DOUBLE.
- Todo:
- Look at the code and find the reference where this is documented. It's not simply central differences, but rather central differences including the next neighbours.
- Parameters
-
sig Contains the 2D signal. retValue After returning true, retValue contains the x and y components of grad(sig). retValue must be of the same size as sig in x and y dimensions and its channel-count must be 2.
- Returns
- True if successful, false otherwise.
◆ hypot()
| Real goMath::hypot | ( | const Real & | a, |
| const Real & | b | ||
| ) |
- Returns
- hypotenuse of real (non-complex) scalars a and b by avoiding underflow/overflow using (a * sqrt( 1 + (b/a) * (b/a))), rather than sqrt(a*a + b*b).
◆ integrate()
| T goMath::integrate | ( | const goMath::Vector< T > & | v | ) |
Sehnentrapezformel. Step width (h) is assumed 1, so normalisation may be needed afterwards.
- Parameters
-
v Vector with function values at equidistant points.
- Returns
- Integral approximation.
◆ integrateSimpson()
| T goMath::integrateSimpson | ( | const goMath::Vector< T > & | v | ) |
Integration with Simpson rule. Step width h is assumed 1, so normalisation may be needed afterwards.
The composite Simpson rule is 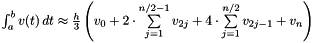 , if the continuous function v(t) is divided into an even number n of equidistant intervals with distance h. Note that
, if the continuous function v(t) is divided into an even number n of equidistant intervals with distance h. Note that integrateSimpson samples linearly between points given in v to obtain an even number of sampled points. Also, only the division by 6 (not 3!) is done, since the step width h is assumed to be one. Normalisation may therefore be done after calling this function by the user, e.g. if the interval [a,b] has length one, by multiplying with 1/v.getSize().
- Parameters
-
v Vector with function values at equidistant points.
- Returns
- Integral approximation.
◆ karcherMean()
| bool goMath::karcherMean | ( | iterator_type | start, |
| int | count, | ||
| manifold_type & | manifold, | ||
| typename manifold_type::Element & | meanRet, | ||
| int | max_iterations = 1000, |
||
| double | epsilon = 1e-6 |
||
| ) |
Karcher mean for generic Riemannian manifolds.
The Karcher mean is calculated by iterating using the update step 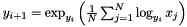 until
until max_iterations has been reached or until 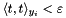 , with
, with 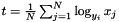 .
.
- Parameters
-
start Start iterator, pointing to the first element x_j. count Number of elements N. manifold Manifold object (e.g. SO3). meanRet Return value, contains the mean after returning true. max_iterations Max. number of iterations. Default: 1000 epsilon "Small" floating point value. Default: 1e-6
- Returns
- True if mean could be found within max_iterations, false otherwise.
- Examples
- karchermean/km.cpp.
◆ laplacian2D()
| bool goMath::laplacian2D | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | sig, |
| goSignal3DBase< void > & | retValue | ||
| ) |
Calculates the laplacian (2nd derivative) of a 2D signal (z-size == 1).
- Note
- The data type of the arguments is currently restricted to GO_FLOAT, but GO_DOUBLE will also be implemented. Multichannel data is not yet supported by libGo.
- Parameters
-
sig Contains the 2D signal. retValue After returning true, retValue contains the laplace(sig). retValue must be of the same size as sig in x and y dimensions and its z dimension must be 1.
- Todo:
- BUG: This sometimes can produce NaNs.
- Returns
- True if successful, false otherwise.
◆ matrixVectorMult() [1/4]
|
inline |
(this) * v
- Parameters
-
ret
v
- Returns
◆ matrixVectorMult() [2/4]
|
inline |
(this) * v
- Parameters
-
ret
v
- Returns
◆ matrixVectorMult() [3/4]
|
inline |
(this) * v
- Parameters
-
ret
v
- Returns
◆ matrixVectorMult() [4/4]
|
inline |
(this) * v
- Parameters
-
ret
v
- Returns
◆ max()
| Scalar goMath::max | ( | Scalar | a, |
| Scalar | b | ||
| ) |
- Returns
- the maximum of scalars a and b.
◆ min()
| Scalar goMath::min | ( | Scalar | a, |
| Scalar | b | ||
| ) |
- Returns
- the minimum of scalars a and b.
◆ mod()
| T goMath::mod | ( | T | value, |
| T | modulus | ||
| ) |
Modulus function.
- Parameters
-
value modulus
- Returns
valuemodmodulus
◆ paste2D()
| void goMath::paste2D | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | source, |
| goDouble | scale, | ||
| goDouble | angle, | ||
| goDouble | t_x, | ||
| goDouble | t_y, | ||
| goSignal3DBase< void > & | target, | ||
| goFloat | bgColour | ||
| ) |
Paste source at under some euclidean transformations into target.
- Parameters
-
source Source patch scale scale factor angle rotation angle t_x Translation x t_y Translation y target target signal (is left unchanged except for the pasted source)bgColour Transparent colour in source. Only points which have different colour values are pasted intotarget.
◆ resampleCubic()
| bool goMath::resampleCubic | ( | const goMath::Matrix< T > & | source, |
| goMath::Matrix< T > & | target, | ||
| goSize_t | resamplePointCount, | ||
| bool | closed = false, |
||
| goFixedArray< goDouble > * | accumLength_ = 0 |
||
| ) |
Piecewise cubic resampling of a curve represented by a configuration matrix.
The source matrix contains a point in each row, so does the target matrix after successful completion of the function.
- Parameters
-
source Source points. target Target points. resamplePointCount Point count intended for target. closed If true, the source points will be treated as a closed curve, i.e. the first and last points are connected.
- Returns
- True if successful, false otherwise.
◆ scale2D()
| void goMath::scale2D | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | source, |
| goSignal3DBase< void > & | target, | ||
| bool | keep_aspect = false |
||
| ) |
Scale source into target.
- Todo:
- Extend to 3D – this only requires to write a 3D sampling function.
- Parameters
-
source Original 2D signal target Target 2D signal keep_aspect If true, keep aspect ratio
◆ set()
|
inline |
Not implemented.
A general set function would require some reallocating and copying of arrays. I had no use for that so far, but please implement it AND GIVE IT BACK TO ME if you need it.
- Parameters
-
row
col
v
◆ sortColumns()
|
inline |
Sorts in ascending column order.
Sorts all elements so that they appear in ascending column order in the internal arrays.
◆ sortRows()
|
inline |
Sorts in ascending row order.
Sorts all elements so that they appear in ascending row order in the internal arrays.
◆ stencil()
| T goMath::stencil | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | sig, |
| const goMath::Matrix< T > & | s | ||
| ) |
Calculate 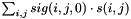 .
.
Can be used to calculate a sum of a 2D stencil multiplied by the values in sig. Only the z=0 plane is accounted for in sig. You can for example have a goSubSignal3D move over a goSignal3DBase and calculate some weighted sum (in 2D) at each point of interest.
The sizes of sig and s should match.
- Parameters
-
sig Signal s Matrix containing the stencil.
- Returns
- The sum of the elements in
sigweighted withs.
◆ transform2D()
| void goMath::transform2D | ( | const goSignal3DBase< void > & | source, |
| goDouble | scale, | ||
| goDouble | angle, | ||
| goDouble | t_x, | ||
| goDouble | t_y, | ||
| goSignal3D< void > & | target, | ||
| bool | setsize = true |
||
| ) |
2D euclidean transformation of an image.
Calculate 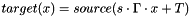
- Parameters
-
source Source image (2D) scale Scale factor angle Rotation angle t_x Translation in x t_y Translation in y target Target, will be resized and set to the data type of sourceif necessary.setsize Automatically set size of target if it does not fit. Default: true.
◆ vectorMatrixMult() [1/2]
|
inline |
v' * (this)
- Parameters
-
ret
v
- Returns
◆ vectorMatrixMult() [2/2]
|
inline |
v' * (this)
- Parameters
-
ret
v
- Returns
